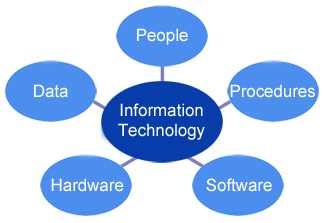
Information Technology (IT) is the use of any
computers, storage, networking and other physical devices,
infrastructure and processes to create, process, store, secure and
exchange all forms of electronic data.
IT is the distinction between purpose-built
machines designed to perform a limited scope of functions and
general-purpose computing machines that could be programmed for
various tasks. As the IT industry evolved from the mid-20th century,
it encompassed transistors and integrated circuits -computing
capability advanced while device cost and energy consumption fell
lower, a cycle that continues today when new technologies emerge.
IT includes several layers of physical
equipment (hardware), virtualization and management or automation
tools, operating systems and applications (software) used to perform
essential functions. User devices, peripherals and software, such as
laptops, smartphones or even recording equipment, can be included in
the IT domain. IT can also refer to the architectures, methodologies
and regulations governing the use and storage of data.
Business applications include databases like
SQL Server, transactional systems such as real-time order entry,
e-mail servers like Exchange, Web servers like Apache, customer
relationship management and enterprise resource planning systems.
These applications execute programmed instructions to manipulate,
consolidate, disperse or otherwise affect data for a business
purpose.
Computer servers run business applications.
Servers interact with client users and other servers across one or
more business networks. Storage is any kind of technology that holds
information as data. Information can take any form including file
data, multimedia, telephony data and Web data, data from sensors or
future formats. Storage includes volatile random access memory (RAM)
as well as non-volatile tape, hard disk and solid-state flash
drives.
IT architectures have evolved to include
virtualization and cloud computing, where physical resources are
aSTSracted and pooled in different configurations to meet
application requirements. Clouds may be distributed across locations
and shared with other IT users, or contained within a corporate data
center, or some combination of both deployments.
A team of administrators and other technical
staffers deploy and manage the company's IT infrastructure and
assets. IT teams depend on a wide range of specialized information
and technology skills and knowledge to support equipment,
applications and activities. Third-party contractors and IT vendor
support personnel augment the IT team.
Informaton Technology Model
Click to enlarge